| Anthracnose | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| A parsnip with canker | |
| Synonyms | |
| Anthracnose Canker |
Anthracnose and Canker are general terms for a large number of different plant diseases, characterised by broadly similar symptoms including the appearance of small areas of dead tissue, which grow slowly, often over a period of years. Some are of only minor consequence, but others are ultimately lethal. Different cankers and anthracnoses are caused by a wide range of organisms, including fungi, bacteria, mycoplasmas and viruses. This does not usually render the roots inedible. It can be caused by several factors - Soil acidity, presence of fresh organic matter in the soil, root damage and irregular rainfall.
Important Species[]
Important species susceptible to anthracnose[1]:
- Anthracnose of Cucurbits (Colletotrichum orbiculare)
- Anthracnose of raspberry (Elsinoe veneta)
- Anthracnose of tomato (Colletotrichum coccodes, Colletotrichum phomoides)
- Banana anthracnose (Colletotrichum musae)
- Bean anthracnose (Colletotrichum lindemuthianum)
- Corn anthracnose (Glomerella graminicola)
- Grape canker (Eutypa lata)
- Onion smudge (Colletotrichum circinans)
- Pepper anthracnose (Colletotrichum capsici, Colletotrichum dematium)
- Aubergine, Potato & Tomato bacterial canker (Clavibacter michiganensis)
Symptoms[]
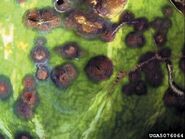
Symptoms are most visible on leaves and ripe fruits. First appears on leaves as small and irregular yellow, brown, dark-brown, or black spots which may expand to cover the whole affected area. Infections darken with age. Can also cause severe defoliation and rotting of fruit and roots. Infected fruit has small, watersoaked, sunken, circular spots that may increase in size up to 1.2 cm in diameter. As it ages, the center of an older spot becomes blackish and emits gelatinous pink spore masses.[1]
Treatment[]
Some cankers are treatable with fungicides or bactericides, but many are not; often the only treatment available is to destroy the infected plant to prevent the disease from spreading to other plants.
Prevention[]
This can be avoided by liming the soil, growing a resistant variety or growing in a sterile soil/compost/sand mixture in deep containers. This is usually the preferred choice for exhibition growers who require long, clean roots.
Examples[]
References[]
- ↑ a b "Anthracnose". PAN Germany. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
| This page uses Creative Commons Licensed content from Wikipedia (view authors). |
| Aubergine troubles |
|
|---|---|
| Adverse conditions | |
| Diseases | Anthracnose · Black dot · Phomopsis blight · Phytophthora blight · Southern bacterial wilt · Southern blight |
| Pests | Aphid · Flea beetle · Greenhouse Whitefly · Pepper weevil · Red spider mite · Southern corn rootworm · Thrips |
| Corn troubles |
|
|---|---|
| Adverse conditions | Drought · Iron deficiency · Magnesium deficiency · Nitrogen deficiency · Nitrogen toxicity · Phosphorous deficiency · Sun scald |
| Diseases | Aspergillus ear and kernel rot · Anthracnose · Bacterial soft rot · Crazy top of corn · Grey leaf spot of corn · Charcoal rot · Corn smut · Corn stunt disease · Fasciation · Fusarium ear and stalk rot · Maize dwarf mosaic virus · Northern corn leaf blight · Pink root of onion · Pythium · Stewart's wilt |
| Pests | Aphid · European corn borer · Cutworm · Leafminer · Root-knot nematode |
| Brassica troubles |
|
|---|---|
| Broccoli · Brussels sprout · Cabbage · Cauliflower · Kale · Kohl rabi · Radish · Swede · Turnip | |
| Adverse conditions | Blown sprouts · Bolting · Boron deficiency · Button cauliflower · Calcium deficiency · Heartless cabbage · Magnesium deficiency · Manganese deficiency · Molybdenum deficiency · Nitrogen deficiency · Split heart |
| Diseases | Anthracnose · Bacterial soft rot · Black leaf spot · Black rot · Brassica dark leaf spot · Club root · Downey mildew · Grey leaf spot (Brassica) · Turnip mosaic virus · Sclerotinia rot · White leaf spot · White leaf spot (Brassica) · White rust · Wire stem |
| Pests | Aphid · Cabbage aphid · Cabbage Moth · Cabbage root fly · Cabbage Whitefly · Cutworm · Diamondback moth · Flea beetle · Large White · Pigeon · Silver Y moth · Slug · Small White · Swede midge · Thrips |
| Raspberry troubles |
|
|---|---|
| Adverse conditions | |
| Diseases | Anthracnose · Cane and leaf rust · Cercosporella leaf spot · Downy mildew · Arabis mosaic virus · Orange rust · Phytophthora root rot of raspberry · Raspberry leaf curl virus · Raspberry leaf spot · Raspberry ringspot virus · Rose scale · Septoria leaf spot of blackberry · Spur blight |
| Pests | Raspberry beetle · Raspberry horntail |